The construction industry plays a crucial role in global energy-related CO2 emissions, making it imperative to prioritize sustainability in this sector. This article explores various initiatives and practices aimed at reducing pollution, promoting sustainable construction, and driving the future of sustainability in the industry.
The construction industry has made significant strides in embracing sustainability concepts over the years. However, there is still ample room for improvement. The first BREEAM certification was launched in 1990, followed by the introduction of LEED certification in 1998. Environmental impact studies gained prominence in the early 2000s, marking a turning point for the industry. As awareness grows, companies are now focusing more than ever on finding innovative solutions to address ongoing challenges and reduce their environmental footprint.
Still, the construction sector is responsible for 37% of total global energy-related CO2 emissions, according to the World Economic Forum, based on the 2021 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction. Alarmingly, 69% of these emissions arise from the operation and utilization of existing buildings. Recognizing the urgent need for change, stakeholders are now prioritizing the decarbonization of the EU’s economy, with the building sector at the forefront of their efforts. During our attendance at BAU, a trade fair for architecture, materials and systems, one of our content managers, Hannah Boston, identified several companies focused on the new era of construction.
Circular: ReStart – Revolutionizing Material Recovery
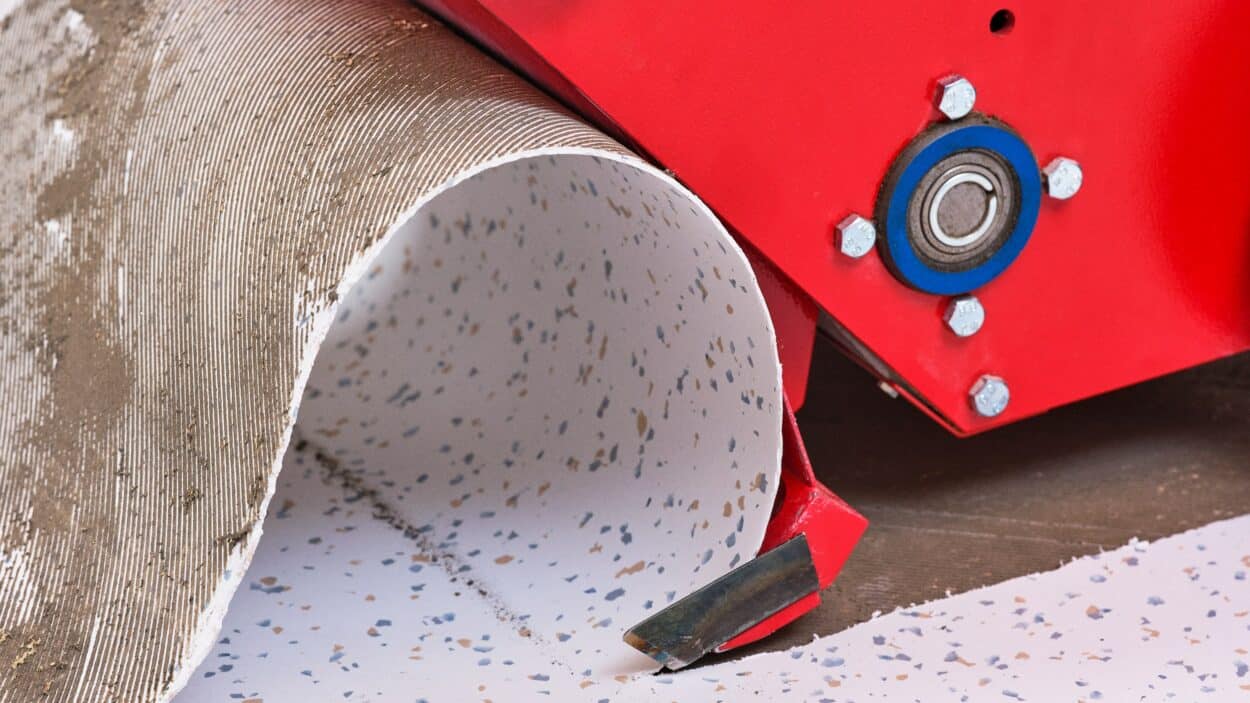
The French group Tarkett, as a flooring and sports surfaces manufacturer, recognized a need to recover construction materials. In 2010, it created its ReStart program for the collection and recovery of flooring. In 2016, the group collaborated with Veolia to help accelerate the deployment of its ReStart® program. Veolia, a leader in recycling and waste management, collects and sorts resilient post-installation flooring off-cuts from Tarkett’s customers in the building industry. The collected and sorted flooring is recycled in Tarkett’s production sites.
The Tarkett Group has been evolving since its founding in 1880, originally under the name Sommer. Today, the company has plunged forward in its objectives to contribute to a more sustainable future which includes its Tarkett Climate School, a digital learning journey to educate its team on sustainability. For its exhibition at BAU, the company took the opportunity to highlight its dedication to eco-design and Cradle-to-Cradle principles through the creation of its booth.

The BAU event organizers explained the focus would be on the fundamental paradigm shift needed in the construction industry, including alternative building materials and digital technology. The Tarkett booth illustrated circular materials in terms of both content and design. Following the event, the company has reused or recycled much of the booth—including the material sample boards, the homogenous vinyl, linoleum and DESSO carpet tiles used for the flooring construction and for the walls of the structure. On display, the brand featured several products from its Circular Selection such as the iD Click, a lock-together luxury tile flooring; the DESSO Fuse landscape, a natural gradient carpet tile flooring for workspaces; and the IQ Granit, a vinyl flooring for education and healthcare facilities, and the IQ eminent which has a polished stone look.




Schüco: Carbon Control and Digital Twin Services
With Carbon Control, the Bielefeld-based company Schüco is offering a modular range of various products and services over the entire lifecycle of a building—planning, construction, operation and dismantling. Professionals involved in the construction process can use this tool to manage the construction of climate-friendly building envelopes. The tool enables the decarbonization of windows, doors and façades to be monitored on a project-specific basis. In addition to the products and services offered by Schüco, the tool also includes project-specific advice and support provided by a team of Carbon Consultants, which will help architects, developers and fabricators to actively minimize the carbon footprint of the building envelope.
The Global Warming Potential (GWP) value results from the interaction between operational carbon emissions and embodied carbon emissions. Operational carbon emissions arise during the operation of a building, while embodied carbon emissions show how much CO2 is embodied in the materials used. The conservative use of material resources, building-integrated photovoltaics, intelligent building management systems or Cradle-to-Cradle-certified products can reduce overall emissions.
Schüco also had digital twin elements available for its products. With Internet of Façades and the IoF ID, the company supplies components of digital building envelopes of its products—windows, doors, façades and sliding systems. Each element of a building is given its own digital identity by a small badge. All data, information, documents and service messages for an element are stored on the badge and are available for the life cycle of the element.
Reducing Carbon Footprint in Concrete Production with Holcim
Holcim creates innovative and sustainable building solutions with a mission to decarbonize construction and is especially interested in reducing the carbon footprint in concrete production. Its portfolio includes a broad range of low-carbon and circular solutions such as its ECOPlanet collection in which it offers Susteno, launched in Switzerland as the world’s first cement containing 20% recycled construction and demolition waste. The only resource-saving cement in Europe, Susteno limits natural resource use and reduces the amount of rubble sent to landfill. The ECOPlanet range of low-carbon cement materials reduces CO2 emissions by at least 30% and is aligned with the world’s highest standards of sustainable building certifications from BREEAM to LEED.
Similarly, ECOPact concrete contains an innovative mix of supplementary cementitious materials and admixture technology, making a low-carbon concrete product range that can reduce the embodied carbon of buildings, infrastructure and homes by at least 30% without offsets. ECOPact is locally produced, recyclable and supports a circular economy. Where norms allow, it can include recycled construction and demolition materials, enhancing its environmental benefits by saving natural resources.
Additionally, Holcim launched ECOCycle, a proprietary circular technology platform to recycle construction demolition materials into new building solutions. All products with ECOCycle® inside contain from 10% to 100% construction demolition materials. The company recycled nearly 7 million tons of construction demolition materials last year and aims to reach at least 10 million tons by 2025.
READ: ECOCycle Enables the World’s First Fully Recycled Concrete Building
A 220-unit social housing complex called “Recygénie” is currently under construction outside Paris, France. Built in partnership with Seqens and using a custom concrete made with Holcim’s ECOCycle® technology, this is the first fully recycled concrete building in the world.
Holcim is also known for its technology Ductal® UHPC, a range of ultra-high-performance, lightweight concrete. The technology was used for projects such as the Louis Vuitton Foundation and the MuCem.
In 2022, Holcim advanced greatly on its mission to decarbonize buildings. Anywhere from operations to construction and making buildings sustainable in use, Holcim is decarbonizing buildings across their life cycle for a net-zero future.